Everything I learned today centers around a question I still haven't learned the answer to. Can we use groudn wave propagation SnR data between San Francisco, Berkeley, and Stanford to measure soil moisture?
I noticed that the SNR (signal to noise ratio) as measured by the RBN (reverse beacon network) spotting stations went up after we started routinely getting rain last week. First, let's get some data to support what I'm saying. The stations are W6YX, (located in Stanford), W6BB, (located in Berkeley), and NU6XB, (also located in Berkeley). Using Datasette to look at the SNR levels from the three stations for the last three weeks gives
The top two charts, W6BB and W6YX show some trends. The chart for NU6XB, at first glance, actually seems to disprove that the increased ground water had anything to do with better SNR.
In any event, here's the ground moisture data captured over the same time span.
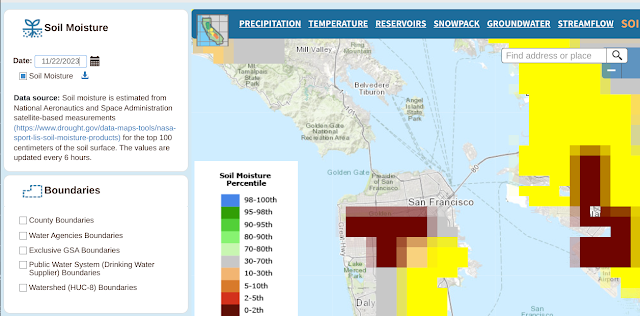
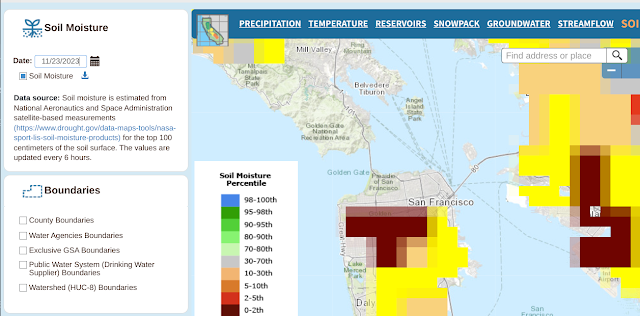
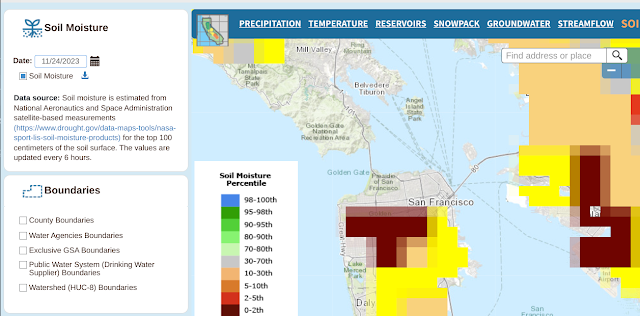
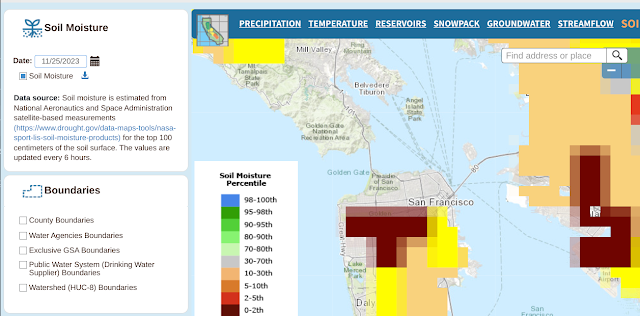


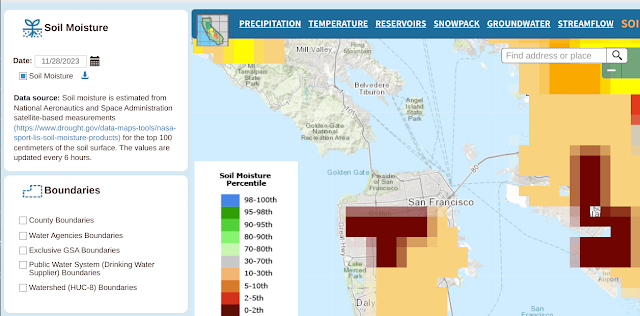
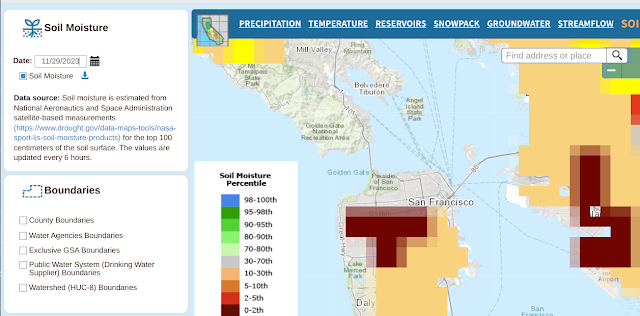
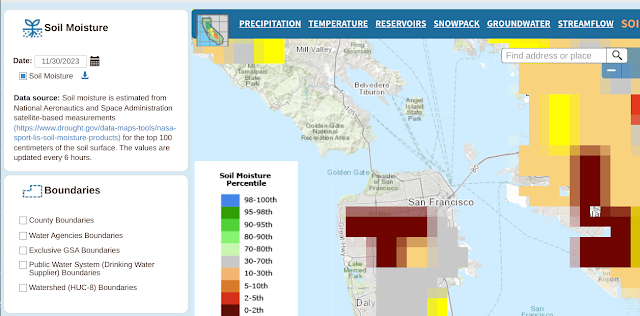

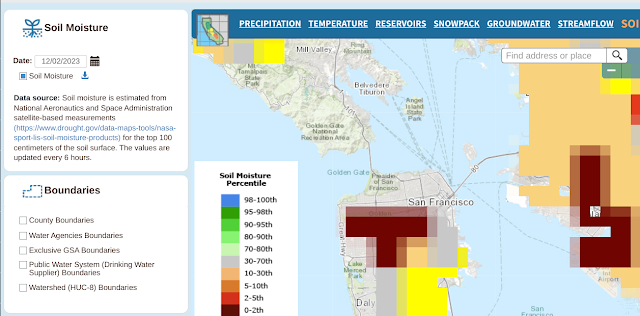
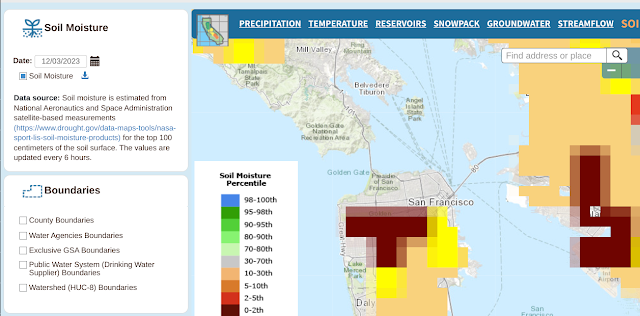
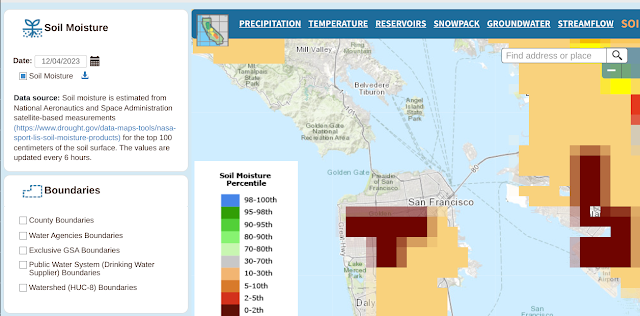
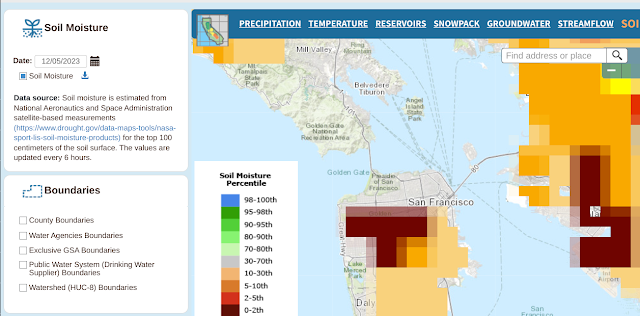
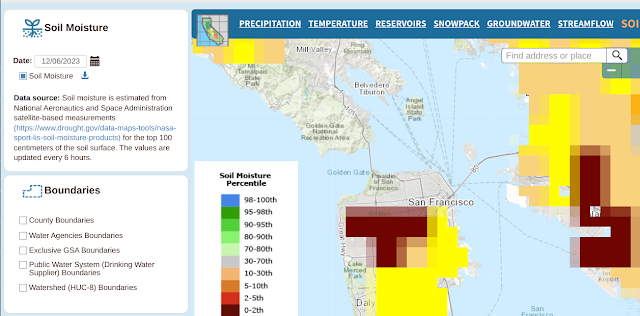
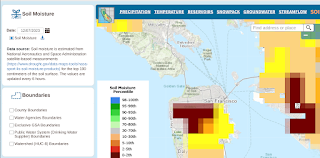
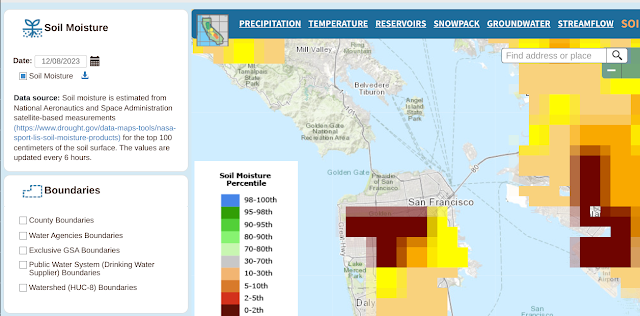
And here are the many, many links to things the gang and I should learn to do more with this:
The important bit: our code so far
The Google Earth Engine REST API so maybe this can all be done in Python
Looks like we'll be using Google Earth Engine, but here's how to rad hf files.
Here's where to get L2 data.
Fundamentals of remote sensing
Soil moisture training
Visualizing ImageCollections
Using Google Earth to visualize soil moisture
The smap L4 layer
It looks like maybe we can get more realtime-ish data by analyzing our own h5 files. Here's a link to the Python script for that. It's pointed to from this page.
Here's how to use something called the Data Access Manger. The pointer came from this rather obscure location.



Comments
Post a Comment
Please leave your comments on this topic: