Why using pytest (or another framework) to test code routinely (as in every time code is added) saves bogs worth of time for developers.
I've found myself running away with adding new features to the reverse beacon network (RBN) mapping project over the last few days. It's been a lot of fun, and now there are prototype maps—for example—that show ionoshperic skip.
It's been a LOT of fun, but I haven't been augmenting my documentation or testing for the project. So, this morning, I earnestly wrote myself a note to read back up on the importance of testing, then I was slammed from my lofty testing heights back to the alley of 'banging out code' by inspiration for a shiny new feature, and I was off.
Fortunately, the note in my journal acted as a positive reinforcment. As I started to write the new feature (animating maps via timestamps in Google Earth), I also popped open an existing pytest file, saved it under a new name, and started writing tests for the new feature.
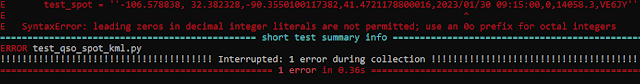
I was immediately rewarded with
OK, so that was an error in the test itself, right? Big deal—in an eye roll sort of way—right? But wait! The next error was


Comments
Post a Comment
Please leave your comments on this topic: