I think I'm finally hitting my studying stride for finals. I can tell because my thoughts on quantum mechanics are starting to merge with the text from Jr.'s Little Golden Books[1], (picture 1). Sure, sure, to some this might mean that I'm studying too much or sleeping too little, but I see it as a sign of some sort of Zen integration of my personal and quantum mechanical lives :) hehehe Hoo Boy!
I hadn't realized it on Friday, but looking back on the whiteboard where my professor kind of wowed me, his solution uses most of the basic tools we were taught this semester in an integrated form rather than as disparate facts which is how they'be been rattling around in my head. So, in the tone of Jr.'s Sesame Street book on helping each other, here goes the solution of "Show that a time dependent force applied to a harmonic oscillator will produce a coherent state. Here's the original white board in all it's glory (picture 2). By the way, the contour integral has nothing to do with the today's coherent state problem.
Jr.'s book contains a set of scenes where someone needs help and then someone provides a solution. You know, something like:
Ernie: "I have a cake that's falling. Who has something that can help a falling cake?"
Cookie Monster has a plate. The cake is now safely ensconced on said plate and Ernie and Cookie Monster are sitting with the plated cake in teh sand box.
Ernie: "Let's eat all the cake!"
OK
Who Knows What a Coherent State Looks Like?
I have the formula for a coherent state! (picture 3)
So, at the end of the day, we need to get some equation of the system to look like the above. It should be in an exponential form and utilize the creation, (a dagger), and annihilation, (a), operators. Lambda is any complex number
Who Has Something that Can Evolve a QHO Subjected to a Time Dependent Force?
I have a unitary time evolution operator!
This is where the time dependence of the problem gets introduced, one of the things I had no idea how to do the first time through the homework problem. It makes perfect sense in retrospect. You're going to need to evolve your system in time, so why not apply the time dependent translation operator, (from the driving force also known as T epsilon of t), to the known unitary time evolution operator for the un-driven system, U naught? (picture 4). As a note, epsilon of t is the function that describes the additional displacement, (due to the time dependent force), of the harmonic oscillator as a function of time.
Who Has a Way to Make a Translation Look Like and Exponent?
I remember the translation operator is an exponent! And! The harmonic oscillator momentum contains the creation and annihilation operators!
Here's the Coup de grâce. The translation operator, (the thing that describes how a system moves in space), looks like a momentum plane wave:
And there's exactly what we were looking for! An operation that when applied to the time evolution of the ground state that we already figure out above will be of the form of the coherent state shown above.
Summary
I hadn't previously realize how to put together all the different techniques we'd been taught this semester to solve a problem, or really that I should even try. I know that it sounds somewhat obvious you should try an somewhat ridiculous I hand't thought of the 'whole' of our knowledge as being applicable in concert, but having not seen it done before, it hadn't occurred. I'm sure my experience matches with some cool teaching pedagogy out there. Now that I have seen what can and should be done, hopefully things will go much more smoothly!
Any questions, pointers, or clarifications of the above are as always more than welcome! The following are just some rambling placeholder notes.
Notes on Bethe's Intermediate Quantum Mechanics
The 'big' and 'small' components of the solutions to the Dirac equation are discussed on page 205 of the 1964 edition. This book is from the same series in which Jackson wrote his math of quantum mechanics book. Jackson was one of the two editors for the series.
References
1. The Together Book by Dwight, R. and Bradfield, R., ISBN 9780307603159, http://books.google.com/books?id=PtnYAAAACAAJ, 1971, Western Publishing Company
I hadn't realized it on Friday, but looking back on the whiteboard where my professor kind of wowed me, his solution uses most of the basic tools we were taught this semester in an integrated form rather than as disparate facts which is how they'be been rattling around in my head. So, in the tone of Jr.'s Sesame Street book on helping each other, here goes the solution of "Show that a time dependent force applied to a harmonic oscillator will produce a coherent state. Here's the original white board in all it's glory (picture 2). By the way, the contour integral has nothing to do with the today's coherent state problem.
Jr.'s book contains a set of scenes where someone needs help and then someone provides a solution. You know, something like:
Ernie: "I have a cake that's falling. Who has something that can help a falling cake?"
Cookie Monster has a plate. The cake is now safely ensconced on said plate and Ernie and Cookie Monster are sitting with the plated cake in teh sand box.
Ernie: "Let's eat all the cake!"
OK
Who Knows What a Coherent State Looks Like?
I have the formula for a coherent state! (picture 3)
So, at the end of the day, we need to get some equation of the system to look like the above. It should be in an exponential form and utilize the creation, (a dagger), and annihilation, (a), operators. Lambda is any complex number
Who Has Something that Can Evolve a QHO Subjected to a Time Dependent Force?
I have a unitary time evolution operator!
This is where the time dependence of the problem gets introduced, one of the things I had no idea how to do the first time through the homework problem. It makes perfect sense in retrospect. You're going to need to evolve your system in time, so why not apply the time dependent translation operator, (from the driving force also known as T epsilon of t), to the known unitary time evolution operator for the un-driven system, U naught? (picture 4). As a note, epsilon of t is the function that describes the additional displacement, (due to the time dependent force), of the harmonic oscillator as a function of time.
Who Has a Way to Make a Translation Look Like and Exponent?
I remember the translation operator is an exponent! And! The harmonic oscillator momentum contains the creation and annihilation operators!
Here's the Coup de grâce. The translation operator, (the thing that describes how a system moves in space), looks like a momentum plane wave:
Summary
I hadn't previously realize how to put together all the different techniques we'd been taught this semester to solve a problem, or really that I should even try. I know that it sounds somewhat obvious you should try an somewhat ridiculous I hand't thought of the 'whole' of our knowledge as being applicable in concert, but having not seen it done before, it hadn't occurred. I'm sure my experience matches with some cool teaching pedagogy out there. Now that I have seen what can and should be done, hopefully things will go much more smoothly!
Any questions, pointers, or clarifications of the above are as always more than welcome! The following are just some rambling placeholder notes.
Notes on Bethe's Intermediate Quantum Mechanics
The 'big' and 'small' components of the solutions to the Dirac equation are discussed on page 205 of the 1964 edition. This book is from the same series in which Jackson wrote his math of quantum mechanics book. Jackson was one of the two editors for the series.
References
1. The Together Book by Dwight, R. and Bradfield, R., ISBN 9780307603159, http://books.google.com/books?id=PtnYAAAACAAJ, 1971, Western Publishing Company

.jpg)


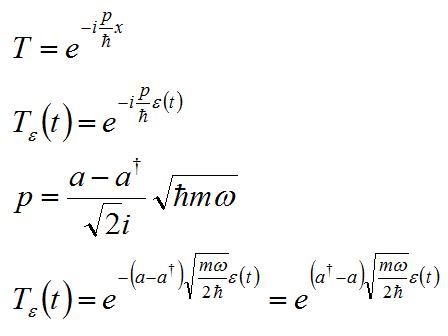
Comments
Post a Comment
Please leave your comments on this topic: